STUDY
DESIGN
Adults with anti-AChR Ab+ and anti-MuSK Ab+ gMG participated in the RYSTIGGO Phase 3 MycarinG clinical trial and in two extension studies1,2
Adults with anti-AChR Ab+ and anti-MuSK Ab+ gMG participated in the RYSTIGGO Phase 3 MycarinG clinical trial and in two extension studies1,2
MycarinG CLINICAL TRIAL
RYSTIGGO was evaluated in a Phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of adults with mild to severe gMG1,2
The efficacy and safety of RYSTIGGO for the treatment of gMG were established in an 18-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase 3 study. In the study, 200 adults with gMG at least 18 years of age were randomized 1:1:1 to receive weight-tiered doses of RYSTIGGO (n=133), either 7 mg/kg of RYSTIGGO (n=66) or 10 mg/kg of RYSTIGGO (n=67), or placebo (n=67). All patients continued on current therapies.1,2
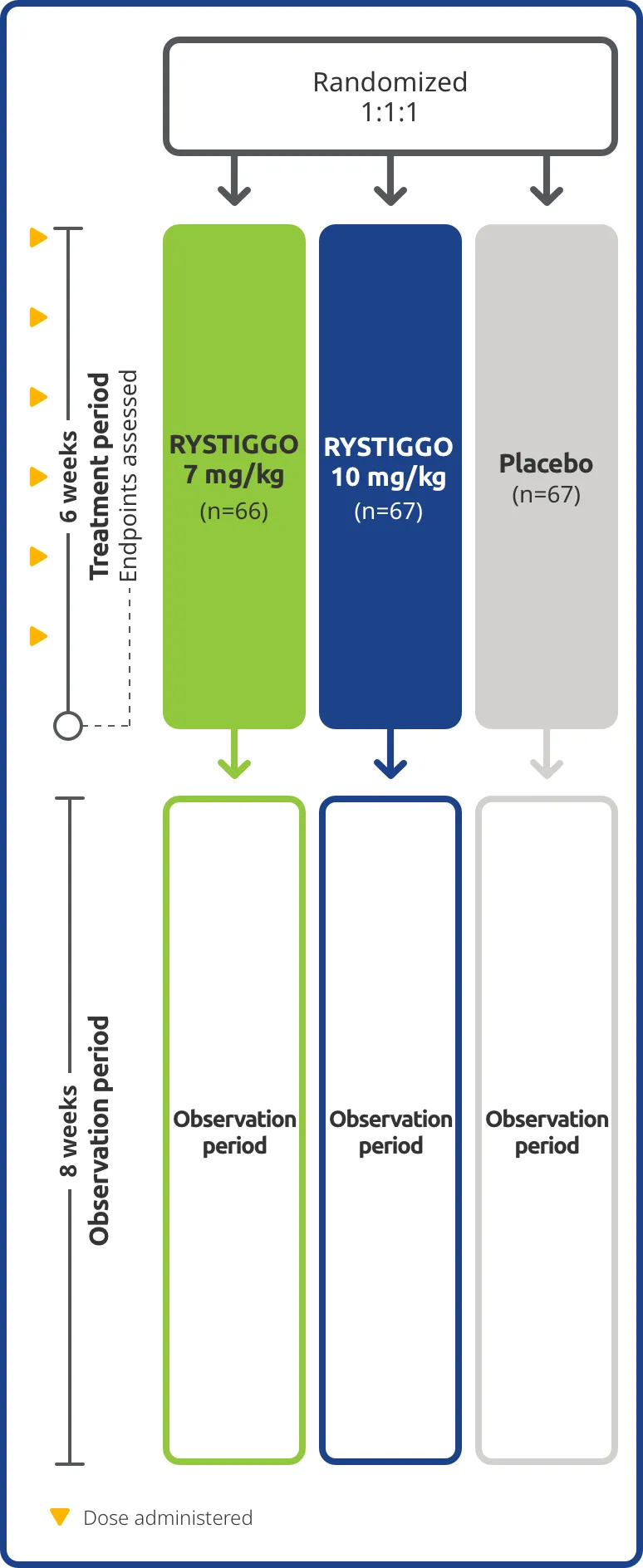
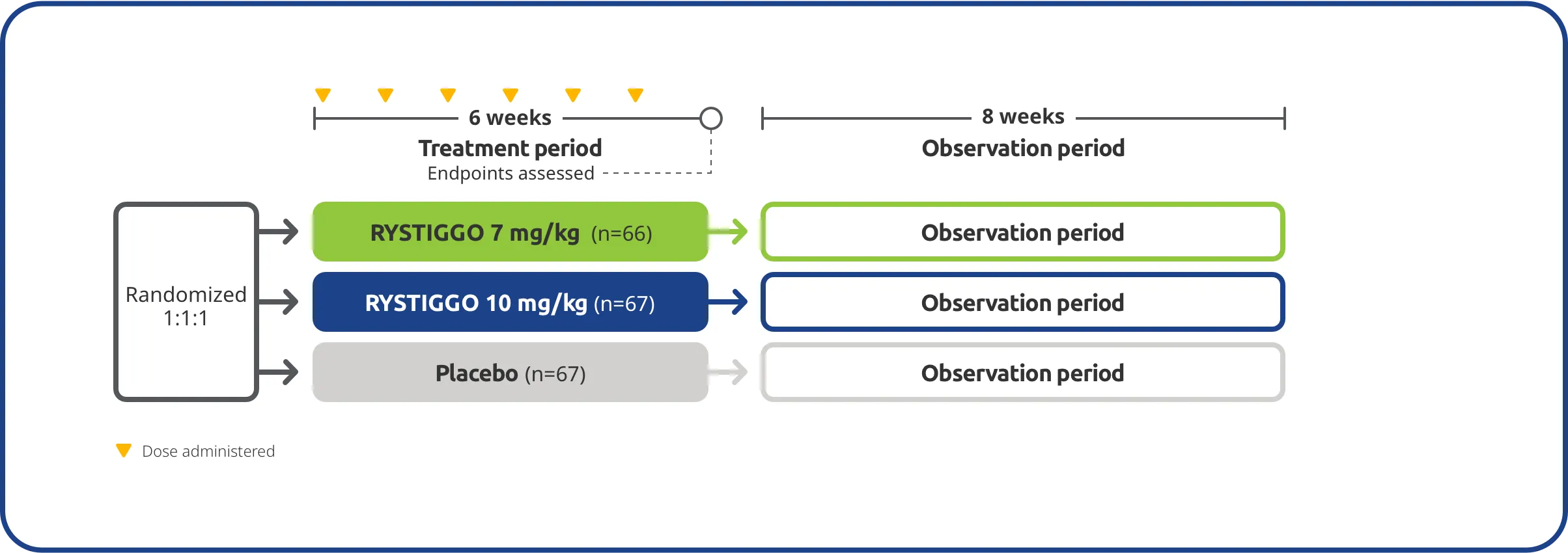
Inclusion criteria1,2
Adults enrolled in the study met the following criteria:
- Presence of autoantibodies against AChR or MuSK
- MGFA Clinical Classification Class II to IVa
- MG-ADL total score of at least 3 (with ≥3 points from non-ocular symptoms)
- On stable dose of MG therapy prior to screening that included AChE inhibitors, steroids, or other NSISTs, either in combination or alone
- Serum IgG levels of at least 5.5 g/L
- QMG score of at least 11
Baseline characteristics2,3
Includes one patient who had unknown AChR and MuSK autoantibody status.2
Includes one patient who had positive AChR and MuSK autoantibody status.2
Patient was classified as MGFA class III at screening, but class IVb at baseline.2
EXTENSION STUDIES
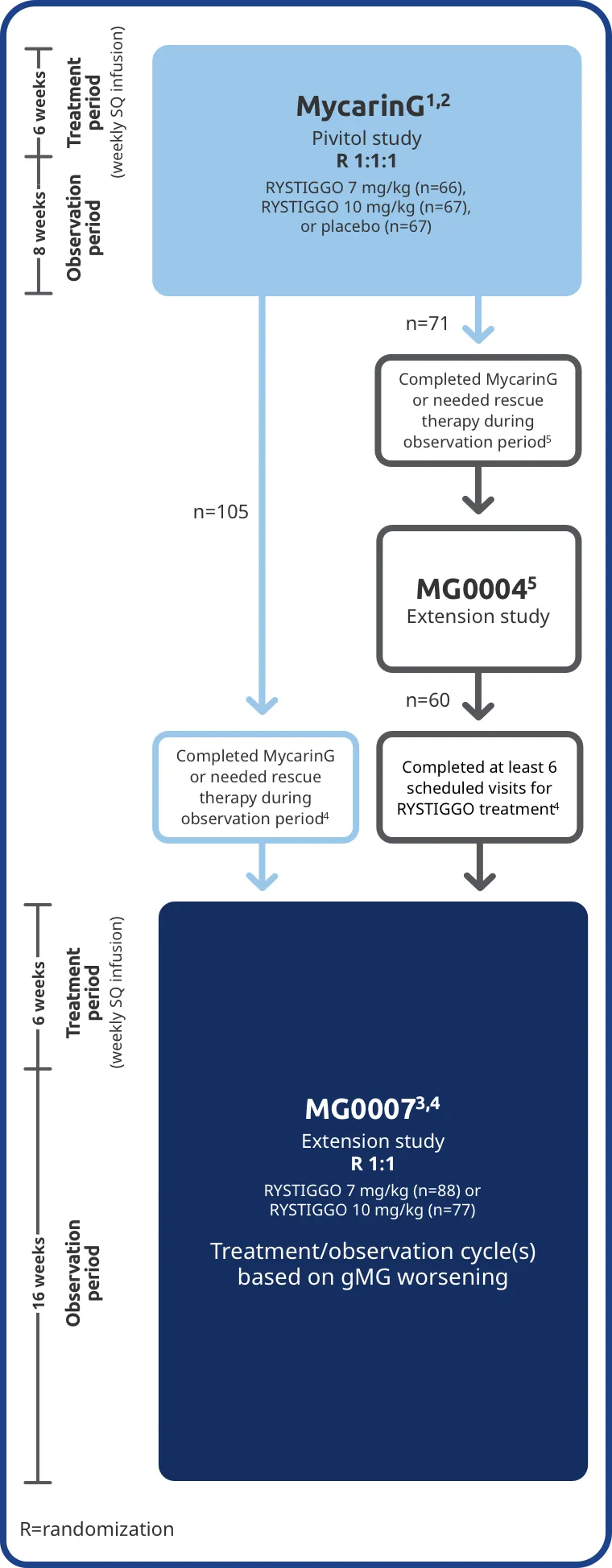
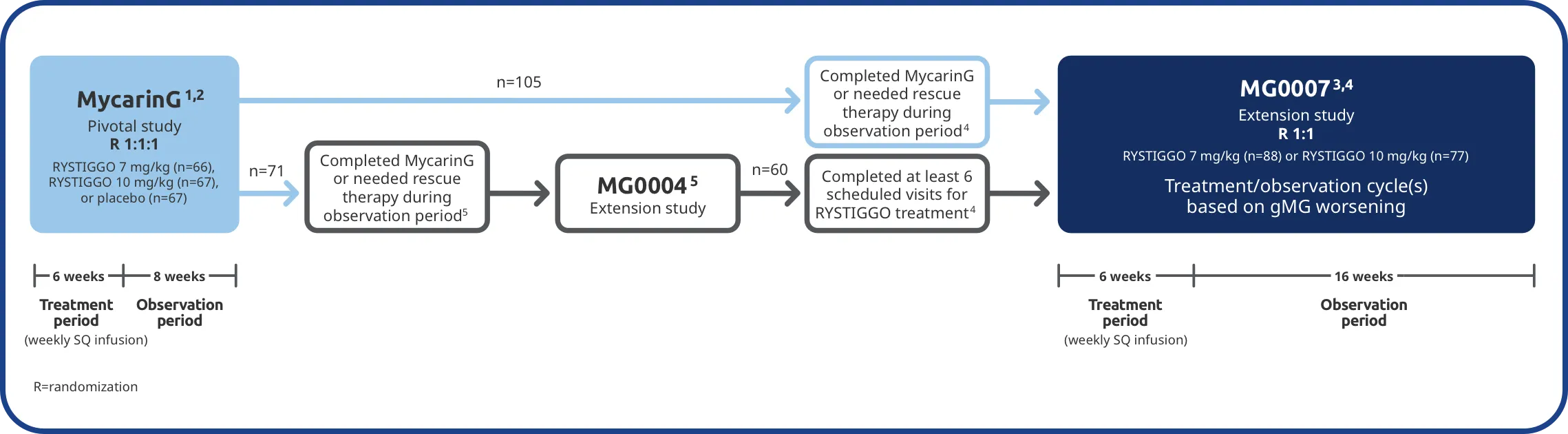
The long-term safety and efficacy of RYSTIGGO was evaluated in adults in two extension studies2,4,5
Patients from the RYSTIGGO treatment groups in MycarinG could enroll in two extension studies, MG0004 and MG0007, that further evaluated the safety and efficacy of RYSTIGGO over time.2,4,5
MG0004 (NCT04124965)
MG0004 was a 60-week, multicenter, randomized, Phase 3 extension study. 71 adult patients from MycarinG who met eligibility criteria were randomized to receive either RYSTIGGO 7 mg/kg or 10 mg/kg. Patients received RYSTIGGO once weekly for a period of up to 52 weeks, followed by 8 weeks of observation. MG0004 enrollment was closed upon the initiation of study MG0007.3,5
MG0007 (NCT04650854)
MG0007 was a multicenter Phase 3 study that included 165 adults from MycarinG and MG0004. It assessed the long-term safety, tolerability, and efficacy of RYSTIGGO given in repeated 6-week cycles, based on the manifestation of gMG symptoms.3,4
Ab+=antibody positive; AChE=acetylcholinesterase; AChR=acetylcholine receptor; gMG=generalized myasthenia gravis; IgG=immunoglobulin G; MG=myasthenia gravis; MG-ADL=Myasthenia Gravis Activities of Daily Living; MGFA=Myasthenia Gravis Foundation of America; MuSK=muscle-specific tyrosine kinase; NSISTs=non-steroidal immunosuppressive therapies; SQ=subcutaneous; QMG=Quantitative Myasthenia Gravis.
References:
- RYSTIGGO [Prescribing Information]. Smyrna, GA: UCB, Inc.
- Bril V, Drużdż A, Grosskreutz J, et al. Safety and efficacy of rozanolixizumab in patients with generalised myasthenia gravis (MycarinG): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, adaptive phase 3 study. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22(5):383-394. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(23)00077-7
- Data on file. UCB Inc., Smyrna, GA.
- A study to evaluate rozanolixizumab in study participants with generalized myasthenia gravis. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04650854. Updated February 26, 2024. Accessed June 6, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04650854
- A study to investigate the long-term safety, tolerability, and efficacy of rozanolixizumab in adult patients with generalized myasthenia gravis. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04124965. Updated September 5, 2023. Accessed June 6, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04124965




